But there are lot of visual editors also available which can produce a suitable UI for your applications. These may be considered as IntelliJ IDEA and some others.
But Android Studio is an official IDE for developing Android App created by Google.
Android Studio and SDK/NDK
Android Studio is the official Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for Android app development, based on IntelliJ IDEA . On top of IntelliJ's powerful code editor and developer tools, Android Studio offers even more features that enhance your productivity when building Android apps, such as:- A flexible Cradle-based build system
- A fast and feature-rich emulator
- A unified environment where you can develop for all Android devices
- Instant Run to push changes to your running app without building a new APK
- Code templates and GitHub integration to help you build common app features and import sample code
- Extensive testing tools and frameworks
- Lint tools to catch performance, usability, version compatibility, and other problems
- C++ and NDK support
- Built-in support for Google Cloud Platform, making it easy to integrate Google Cloud Messaging and App Engine
start for beginner and also for professional in our tutorial.
For this purpose we bring some important things about this here
1. First Step is to download and install.
Setting up Android Studio takes just a few clicks.
Visit the given link and download the latest version of Android Studio.as per your required OS.
Here we only describe installation steps for window OS.
To install Android Studio on Windows, proceed as follows:- If you downloaded an
.exefile (recommended), double-click to launch it. If you downloaded a.zipfile, unpack the ZIP, copy the android-studio folder into your Program Files folder, and then open the android-studio > bin folder and launchstudio64.exe(for 64-bit machines) orstudio.exe(for 32-bit machines). - Follow the setup wizard in Android Studio and install any SDK packages that it recommends
Project structure
Each project in Android Studio contains one or more modules with source code files and resource files. Types of modules include:- Android app modules
- Library modules
- Google App Engine modules
All the build files are visible at the top level under Gradle Scripts and each app module contains the following folders:
- manifests: Contains the
AndroidManifest.xmlfile. - java: Contains the Java source code files, including JUnit test code.
- res: Contains all non-code resources, such as XML layouts, UI strings, and bitmap images.
You can also customize the view of the project files to focus on specific aspects of your app development. For example, selecting the Problems view of your project displays links to the source files containing any recognized coding and syntax errors, such as a missing XML element closing tag in a layout file.
The Android Studio main window is made up of several logical areas identified in below figure
- The toolbar lets you carry out a wide range of actions, including running your app and launching Android tools.
- The navigation bar helps you navigate through your project and open files for editing. It provides a more compact view of the structure visible in the Project window.
- The editor window is where you create and modify code. Depending on the current file type, the editor can change. For example, when viewing a layout file, the editor displays the Layout Editor.
- The tool window bar runs around the outside of the IDE window and contains the buttons that allow you to expand or collapse individual tool windows.
- The tool windows give you access to specific tasks like project management, search, version control, and more. You can expand them and collapse them.
- The status bar displays the status of your project and the IDE itself, as well as any warnings or messages.
At any time, you can search across your source code, databases, actions, elements of the user interface, and so on, by double-pressing the Shift key, or clicking the magnifying glass in the upper right-hand corner of the Android Studio window. This can be very useful if, for example, you are trying to locate a particular IDE action that you have forgotten how to trigger.
Configure Android Studio
Android Studio provides wizards and templates that verify your system requirements, such as the Java Development Kit (JDK) and available RAM, and configure default settings, such as an optimized default Android Virtual Device (AVD) emulation and updated system images. This document describes additional configuration settings you may want to use to customize your use of Android Studio.Android Studio provides access to two configuration files through the Help menu:
studio.vmoptions: Customize options for Studio's Java Virtual Machine (JVM), such as heap size and cache size. Note that on Linux machines this file may be namedstudio64.vmoptions, depending on your version of Android Studio.idea.properties: Customize Android Studio properties, such as the plugins folder path or maximum supported file size.
Find your configuration files
Both configuration files are stored in the configuration folder for Android Studio. The name of the folder depends on your Studio version. For example, Android Studio 2.2 has the folder nameAndroidStudio2.2. The location of this folder depends on your operating system:- Windows:
%USERPROFILE%\.<CONFIGURATION_FOLDER>/ - Mac:
~/Library/Preferences/<CONFIGURATION_FOLDER>/ - Linux:
~/.<CONFIGURATION_FOLDER>/
STUDIO_VM_OPTIONS: set the name and location of the.vmoptionsfileSTUDIO_PROPERTIES: set the name and location of the.propertiesfileSTUDIO_JDK: set the JDK with which to run Studio
Customize your VM options
Thestudio.vmoptions file allows you to customize options for Android Studio's JVM.
To improve Studio's performance, the most common option to adjust is the maximum heap size, but
you can also use the studio.vmoptions file to override other default settings such as
initial heap size, cache size, and Java garbage collection switches.To create a new
studio.vmoptions file or to open your existing one, use the
following steps:- Click Help > Edit Custom VM Options. If you have never
edited VM options for Android Studio before, the IDE prompts you to create a new
studio.vmoptionsfile. Click Yes to create the file. -
The
studio.vmoptionsfile opens in the editor window of Android Studio. Edit the file to add your own customized VM options. For a full list of customizable JVM options, see Oracle's Java HotSpot VM Options page.
studio.vmoptions file you create gets added to the default
studio.vmoptions file, located in the bin/ directory inside your Android
Studio installation folder.Note that you should never directly edit the
studio.vmoptions file found inside the Android Studio program folder. While
you can access the file to view Studio's default VM options, editing only your own
studio.vmoptions file ensures that you don't override important default settings for
Android Studio. Therefore, in your studio.vmoptions file, override only the attributes
you care about and allow Android Studio to continue using default values for any attributes you have
not changed.Maximum heap size
By default, Android Studio has a maximum heap size of 1280MB. If you are working on a large project, or your system has a lot of RAM, you can improve performance by increasing the maximum heap size in the VM options for Android Studio. If your system is memory-constrained, you may wish to reduce the maximum heap size.To change the maximum heap size, follow these steps:
- Click Help > Edit Custom VM Options to open your
studio.vmoptionsfile. - Add a line to the
studio.vmoptionsfile to set maximum heap size using the syntax-XmxheapSize. The size you choose should be based on the size of your project and the available RAM on your machine. As a baseline, if you have more than 4GB of RAM and a medium-sized project, you should set the maximum heap size to 2GB or more. The following line sets the maximum heap size to 2GB:-Xmx2g
-
Save your changes to the
studio.vmoptionsfile, and restart Android Studio for your changes to take effect. -
To confirm your new maximum heap size, open the command line, and type the following command:
jps -lvm
You will see a list of the instrumented JVMs running on your machine, including the full package name for each and the arguments passed in. Locate the item corresponding to your instance of Android Studio. It should end with-Didea.paths.selector=AndroidStudio[Version]. You should see two arguments beginning with-Xmxfor this JVM, one with the default value of 1280mb, and one with your new value, as shown in figure 1.
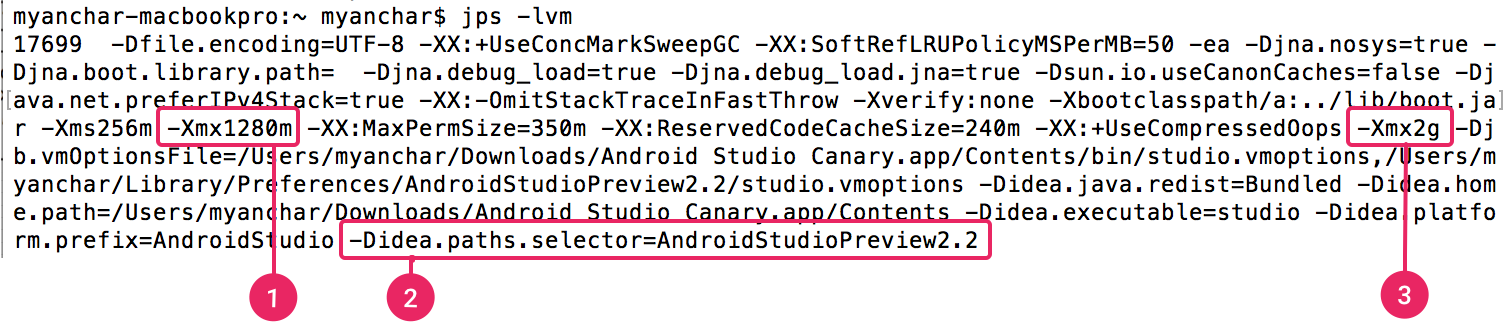 Figure 1. The terminal output showing the current arguments for Android Studio's JVM.
Figure 1. The terminal output showing the current arguments for Android Studio's JVM.-
The
-Xmxargument showing the default maximum heap size, in this case 1280m. -
The
-Didea.paths.selectorshowing the version of Android Studio currently running. -
The
-Xmxargument showing the new custom maximum heap size. Note that this is followed by the location the customstudio.vmoptionsfile you created above.
-
The
Export and import IDE settings
You can export a settings JAR file (Settings.jar) that contains
all or a subset of your preferred IDE settings for a project. You can then import the JAR file
into your other projects and/or make the JAR file available to your colleagues to import into
their projects.
For more information, see Exporting and Importing Settings at IntelliJ IDEA.
Customize your IDE properties
Theidea.properties file allows you to customize IDE properties for Android Studio,
such as the path to user installed plugins and the maximum file size supported by the IDE. The
idea.properties file gets merged with the default properties for the IDE so you can
specify just the override properties.To create a new
idea.properties file or to open your existing file, use the
following steps:- Click Help > Edit Custom Properties. If you have never
edited the IDE properties before, Android Studio prompts you to create a new
idea.propertiesfile. Click Yes to create the file. -
The
idea.propertiesfile opens in the editor window of Android Studio. Edit the file to add your own customized IDE properties.
idea.properties file includes the commonly customized IDE properties.
For a complete list of properties, read about the idea.properties file for IntelliJ IDEA.#--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Uncomment this option if you want to customize path to user installed plugins folder. Make sure # you're using forward slashes. #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # idea.plugins.path=${idea.config.path}/plugins #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Maximum file size (kilobytes) IDE should provide code assistance for. # The larger file is the slower its editor works and higher overall system memory requirements are # if code assistance is enabled. Remove this property or set to very large number if you need # code assistance for any files available regardless their size. #--------------------------------------------------------------------- idea.max.intellisense.filesize=2500 #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # This option controls console cyclic buffer: keeps the console output size not higher than the # specified buffer size (Kb). Older lines are deleted. In order to disable cycle buffer use # idea.cycle.buffer.size=disabled #--------------------------------------------------------------------- idea.cycle.buffer.size=1024 #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Configure if a special launcher should be used when running processes from within IDE. # Using Launcher enables "soft exit" and "thread dump" features #--------------------------------------------------------------------- idea.no.launcher=false #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # To avoid too long classpath #--------------------------------------------------------------------- idea.dynamic.classpath=false #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # There are two possible values of idea.popup.weight property: "heavy" and "medium". # If you have WM configured as "Focus follows mouse with Auto Raise" then you have to # set this property to "medium". It prevents problems with popup menus on some # configurations. #--------------------------------------------------------------------- idea.popup.weight=heavy#--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Use default anti-aliasing in system, i.e. override value of # "Settings|Editor|Appearance|Use anti-aliased font" option. May be useful when using Windows # Remote Desktop Connection for instance. #--------------------------------------------------------------------- idea.use.default.antialiasing.in.editor=false #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Disabling this property may lead to visual glitches like blinking and fail to repaint # on certain display adapter cards. #--------------------------------------------------------------------- sun.java2d.noddraw=true #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Removing this property may lead to editor performance degradation under Windows. #--------------------------------------------------------------------- sun.java2d.d3d=false #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Workaround for slow scrolling in JDK6 #--------------------------------------------------------------------- swing.bufferPerWindow=false #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Removing this property may lead to editor performance degradation under X Window. #--------------------------------------------------------------------- sun.java2d.pmoffscreen=false #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Workaround to avoid long hangs while accessing clipboard under Mac OS X. #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # ide.mac.useNativeClipboard=True #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # Maximum size (kilobytes) IDEA will load for showing past file contents - # in Show Diff or when calculating Digest Diff #--------------------------------------------------------------------- # idea.max.vcs.loaded.size.kb=20480
Configure the IDE for low-memory machines
If you are running Android Studio on a machine with less than the recommended specifications (see System Requirements), you can customize the IDE to improve performance on your machine, as follows:- Reduce the maximum heap size available to Android Studio: Reduce the maximum heap size for Android Studio to 512Mb. For more information on changing maximum heap size, see Maximum heap size.
- Update Gradle and the Android plugin for Gradle: Update to the latest versions of Gradle and the Android plugin for Gradle to ensure you are taking advantage of the latest improvements for performance. For more information about updating Gradle and the Android plugin for Gradle, see the Android plugin for Gradle Release Notes.
- Enable Power Save Mode: Enabling Power Save Mode turns off a number of memory- and battery-intensive background operations, including error highlighting and on-the-fly inspections, autopopup code completion, and automatic incremental background compilation. To turn on Power Save Mode, click File > Power Save Mode.
-
Disable unnecessary lint checks: To change which lint checks Android
Studio runs on your code, proceed as follows:
- Click File > Settings (on a Mac, Android Studio > Preferences) to open the Settings dialog.
- In the left pane, expand the Editor section and click Inspections.
- Click the checkboxes to select or deselect lint checks as appropriate for your project.
- Click Apply or OK to save your changes.
- Debug on a physical device: Debugging on an emulator uses more memory than debugging on a physical device, so you can improve overall performance for Android Studio by debugging on a physical device.
- Include only necessary Google Play services as dependencies: Including Google Play Services as dependencies in your project increases the amount of memory necessary. Only include necessary dependencies to improve memory usage and performance. For more information, see Add Google Play Services to Your Project.
-
Turn on Offline Mode for Gradle: If you have limited bandwitch, turn
on Offline Mode to prevent Gradle from attempting to download missing
dependencies during your build. When Offline Mode is on, Gradle will issue
a build failure if you are missing any dependencies, instead of attempting
to download them. To turn on Offline Mode, proceed as follows:
- Click File > Settings (on a Mac, Android Studio > Preferences) to open the Settings dialog.
- In the left pane, expand Build, Execution, Deployment and then click Gradle.
- Under Global Gradle settings, check the Offline work checkbox.
- Click Apply or OK for your changes to take effect.
-
Reduce the maximum heap size available for Gradle: Gradle's default maximium heap size
is 1,536 MB. Reduce the value by overriding the
org.gradle.jvmargsproperty in thegradle.propertiesfile, as shown below:# Make sure to gradually decrease this value and note # changes in performance. Allocating too lttle memory may # also decrease performance. org.gradle.jvmargs = -Xmx1536m
-
Do not enable parallel compilation: Android Studio can compile
independent modules in parallel, but if you have a low-memory system you
should not turn on this feature. To check this setting, proceed as follows:
- Click File > Settings (on a Mac, Android Studio > Preferences) to open the Settings dialog.
- In the left pane, expand Build, Execution, Deployment and then click Compiler.
- Ensure that the Compile independent modules in parallel option is unchecked.
- If you have made a change, click Apply or OK for your change to take effect.
Configure your project for Instant Run
Instant Run is a behavior for the Run and Debug commands that significantly reduces the time between updates to your app. Although your first build may take longer to complete, Instant Run pushes subsequent updates to your app without building a new APK, so changes are visible much more quickly.Android Studio enables Instant Run by default for projects built using Android plugin for Gradle 2.0.0 and higher. You can improve build performance with Instant Run by modifying a few settings for your project. For more information about configuring your project for Instant Run, read Configure and optimize your project for Instant Run.
Set the JDK version
A copy of the latest OpenJDK comes bundled with Android Studio 2.2 and higher, and this is the JDK version we recommend you use for your Android projects. To use the bundled JDK, proceed as follows:- Open your project in Android Studio and select File > Project Structure in the menu bar.
- In the SDK Location page and under JDK location, check the Use embedded JDK checkbox.
- Click OK.
compileSdkVersion (because different versions of Android support different
versions of Java). If necessary, you can override this default Java version by adding the
following CompileOptions {} block to your build.gradle file:android { compileOptions { sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_6 targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_6 } }For more information about where
compileSdkVersion is defined, read about the module-level build file.Set proxy settings
Proxies serve as intermediary connection points between HTTP clients and web servers that add security and privacy to internet connections.To support running Android Studio behind a firewall, set the proxy settings for the Android Studio IDE. Use the Android Studio IDE HTTP Proxy settings page to set the HTTP proxy settings for Android Studio.
When running the Android plugin for Gradle from the command line or on machines where Android Studio is not installed, such as continuous integration servers, set the proxy settings in the Gradle build file.
Note: After the initial installation of the Android Studio bundle,
Android Studio can run with internet access or off-line. However, Android Studio requires an
internet connection for Setup Wizard synchronization, 3rd-party library access, access to remote
repositories, Gradle initialization and synchronization, and Android Studio version updates.
Set up the Android Studio proxy
Android Studio supports HTTP proxy settings so you can run Android Studio behind a firewall or secure network. To set the HTTP proxy settings in Android Studio:- From the menu bar, click File > Settings (on a Mac, click Android Studio > Preferences).
- In the left pane, click Appearance & Behavior > System Settings > HTTP Proxy. The HTTP Proxy page appears.
- Select Auto-detect proxy settings to use an automatic proxy configuration URL for the proxy settings or Manual proxy configuration to enter each of the settings yourself. For a detailed explanation of these settings, see HTTP Proxy.
- Click Apply or OK for your changes to take effect.
Android plugin for Gradle HTTP proxy settings
When running the Android plugin from the command line or on machines where Android Studio is not installed, set the Android plugin for Gradle proxy settings in the Gradle build file.For application-specific HTTP proxy settings, set the proxy settings in the
build.gradle file as required for each application module.apply plugin: 'com.android.application' android { ... defaultConfig { ... systemProp.http.proxyHost=proxy.company.com systemProp.http.proxyPort=443 systemProp.http.proxyUser=userid systemProp.http.proxyPassword=password systemProp.http.auth.ntlm.domain=domain } ... }For project-wide HTTP proxy settings, set the proxy settings in the
gradle/gradle.properties file. # Project-wide Gradle settings. ... systemProp.http.proxyHost=proxy.company.com systemProp.http.proxyPort=443 systemProp.http.proxyUser=username systemProp.http.proxyPassword=password systemProp.http.auth.ntlm.domain=domain systemProp.https.proxyHost=proxy.company.com systemProp.https.proxyPort=443 systemProp.https.proxyUser=username systemProp.https.proxyPassword=password systemProp.https.auth.ntlm.domain=domain ...For information about using Gradle properties for proxy settings, see the Gradle User Guide.





